
MIGRATION FROM MULTILAYER MATERIALS
MIGRATION FROM MULTILAYER MATERIALSFunctional barriers3D descriptionTrue Multilayer materialsOverviewMigration kinetics are more complex than in monolayer casesEquilibrium concentrationsConservative assumptions for risk assessmentRemoving reservoir layersChanging chemical potentialsExamples: trilayer AbCRefined scenarios: trilayer AbC
Functional barriers
Text from EU regulation 10/2011/EC
(27) In recent years plastic food contact materials are being developed that do not only consist of one plastic but combine up to 15 different plastic layers to attain optimum functionality and protection of the food, while reducing packaging waste. In such a plastic multi-layer material or article, layers may be separated from the food by a functional barrier. This barrier is a layer within food contact materials or articles preventing the migration of substances from behind that barrier into the food.
Behind a functional barrier, non-authorised substances may be used, provided they fulfil certain criteria and their migration remains below a given detection limit. Taking into account foods for infants and other particularly susceptible persons, as well as the large analytical tolerance of the migration analysis, a maximum level of 0,01 mg/kg in food should be established for the migration of a non-authorised substance through a functional barrier. Substances that are mutagenic, carcinogenic or toxic to reproduction should not be used in food contact materials or articles without previous authorisation and should therefore not be covered by the functional barrier concept. New technologies that engineer substances in particle size that exhibit chemical and physical properties that significantly differ from those at a larger scale, for example, nanoparticles, should be assessed on a case-by-case basis as regards their risk until more information is known about such new technology. Therefore, they should not be covered by the functional barrier concept.
Comparatively to monolayer materials, Kinetics are not necessarily homothetic but they can be sill compared for a same Fourier time if a reference layer.
Property description SI units contact time diffusion coefficient (in the reference layer) wall thickness of the reference layer (do not choose the functional barrier () as reference layer, if you want to compare with and without )
3D description
The functional barrier () is made from the same material as the reference one (). In other words, the migrant is distributed uniformly in the reference layer and absent in the

True Multilayer materials
Layers have different properties. It is convenient to choose for the food and to index the layer in contact with food.
concentration of substance in layer Henry-like coefficient of substance in layer Diffusion coefficient of substance in layer when Henry-like coefficients relate the partial pressure of the substance in layer , denoted with its local concentration as:
The partition coefficient between the layer and can be expressed with values by noting that partial pressures are equal at thermodynamical equilibrium ():
Choosing arbitrarily =1 enables to identify all Henry-like coefficients with the partition coefficient with food .
Overview

Migration kinetics are more complex than in monolayer cases
delayed kinetics
slowed kinetic
non-monotonic behavior
Concentration profiles
Migration kinetics
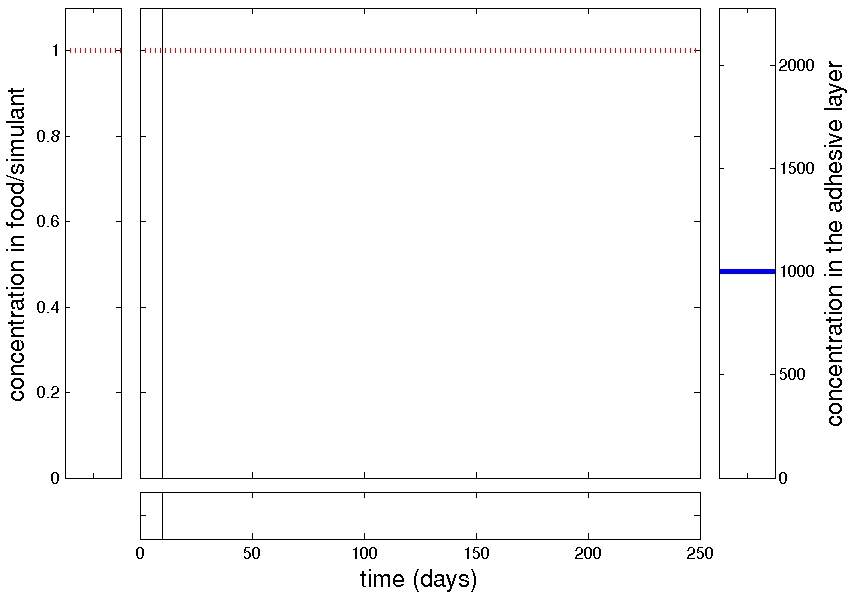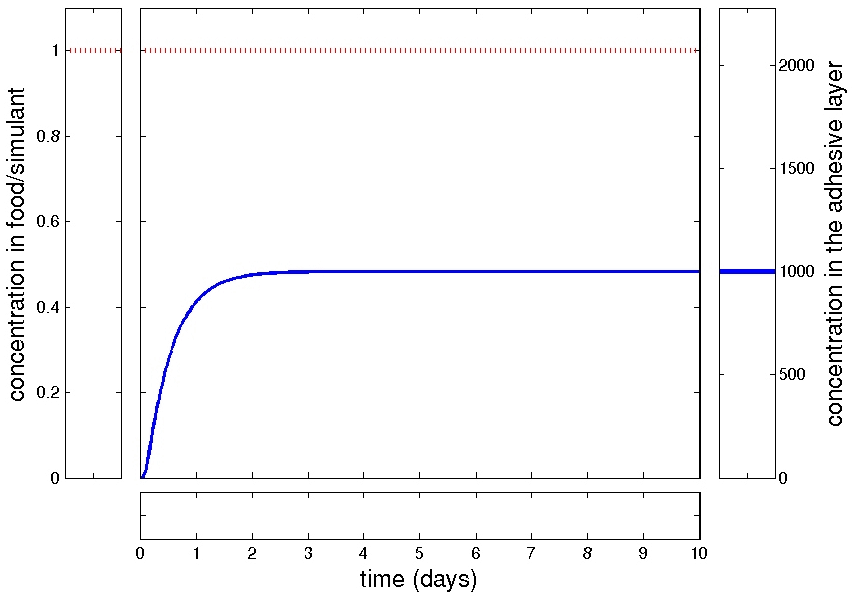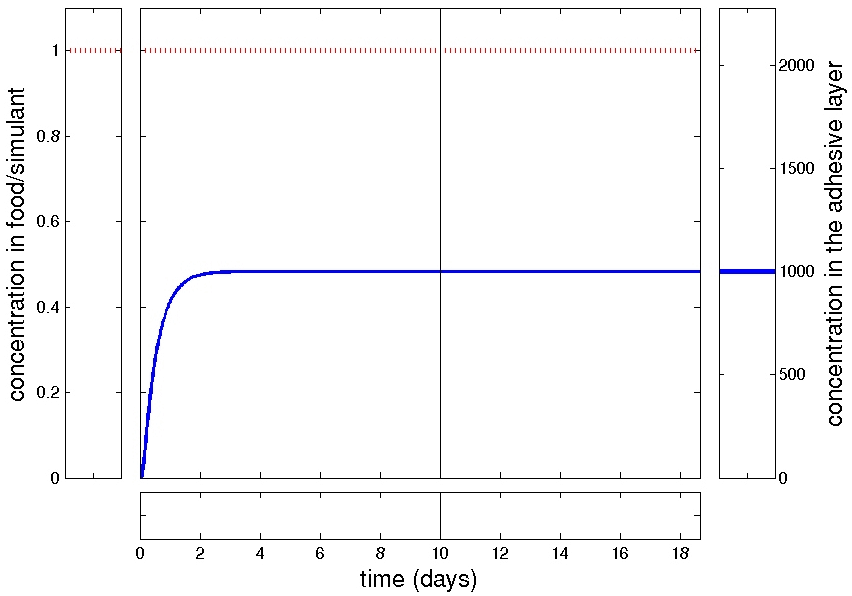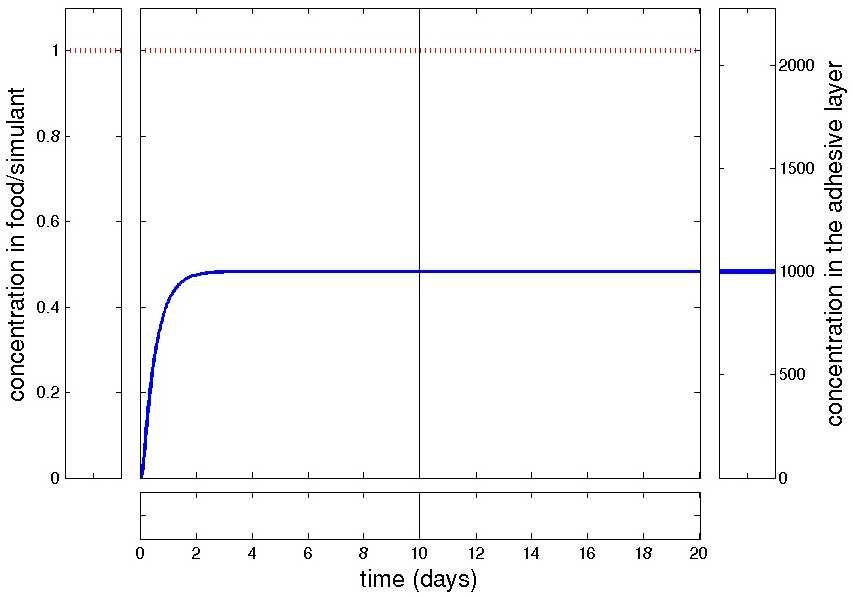
delayed kinetics
slowed kinetics
non-monotonic behavior
delayed kinetics
slowed kinetics
non-monotonic behavior
Equilibrium concentrations
Conservative assumptions for risk assessment
General principles
Since all equations are linear with concentrations, the solution associated to layers is the sum of solutions where only one layer is initially formulated at a time. The sum can be constructed in a way that a conservative solution is calculated with less unknowns.
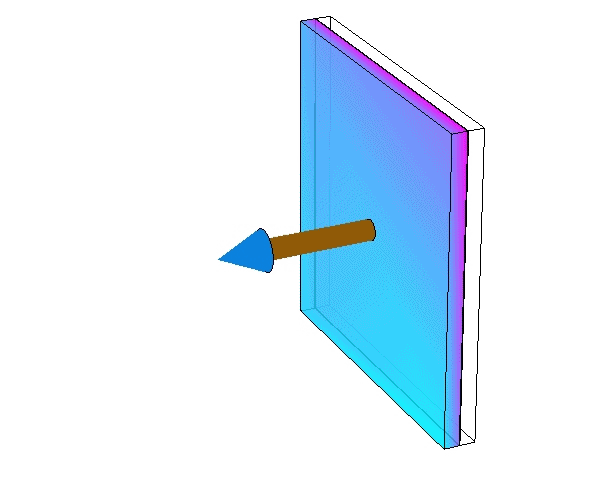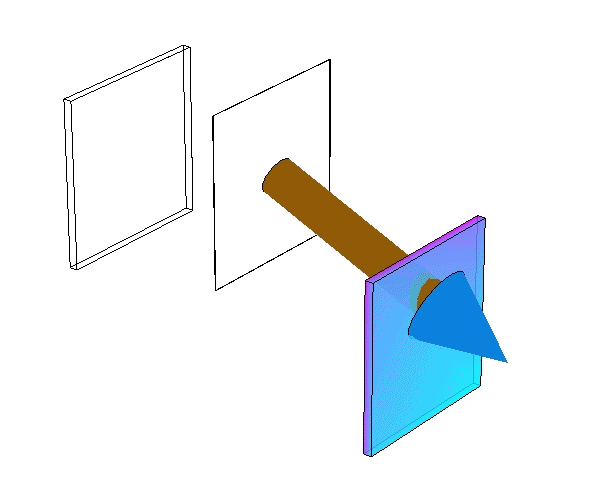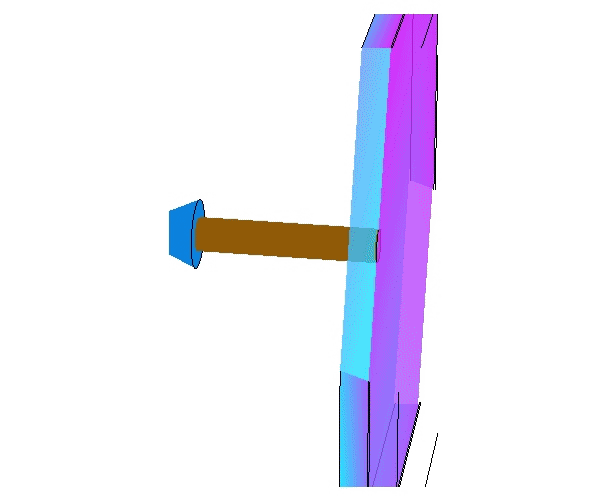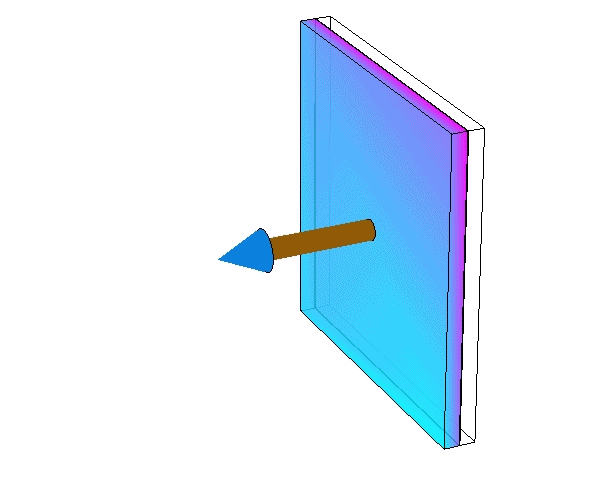
- A layer indexed is called if it is behind the formulated layer (i.e. it can be safely removed or it is always safe to assume ).
- A layer indexed is called when it is located in front of the layer (i.e. it cannot be removed, but it always safe to consider )
- Sequential simulation (for different initial solutions) or the construction of a conservative initial solution enables to construct first tier scenarios even in presence of strong uncertainty on partition coefficients.
Removing reservoir layers
| reality | conservative | even more conservative |
|---|---|---|
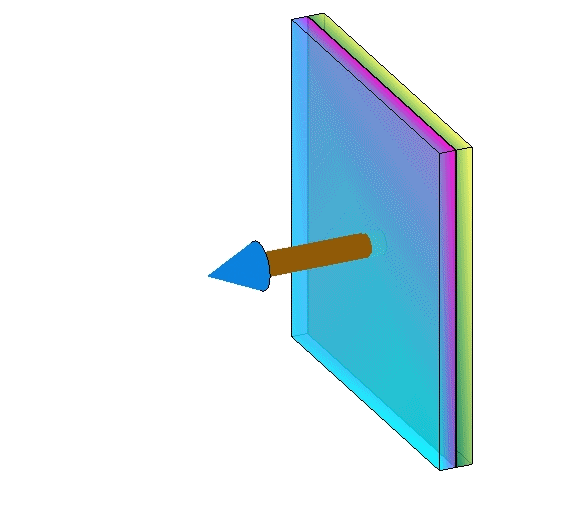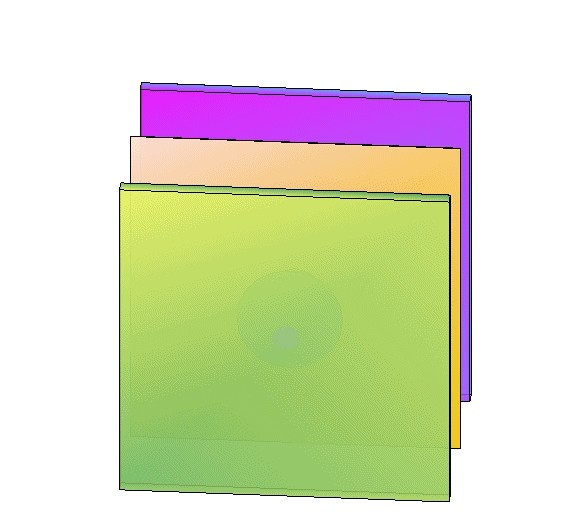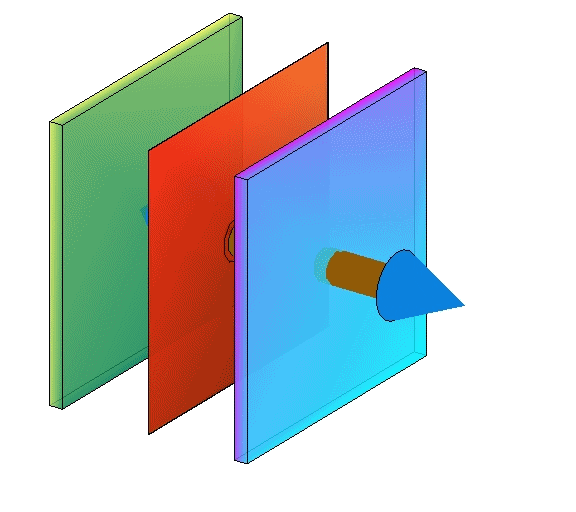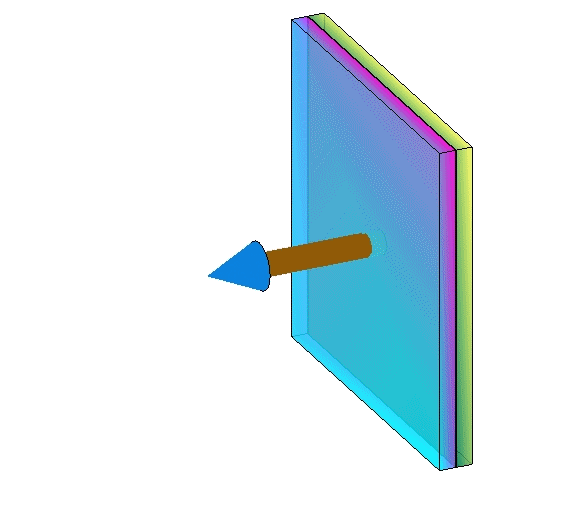 | 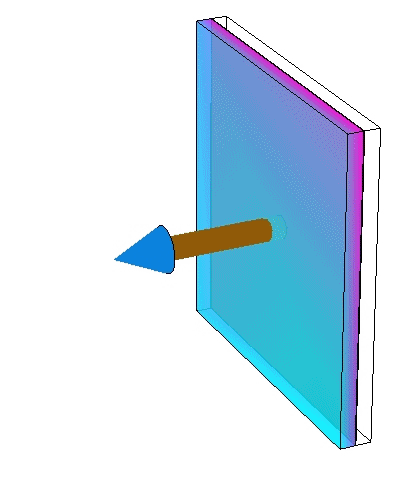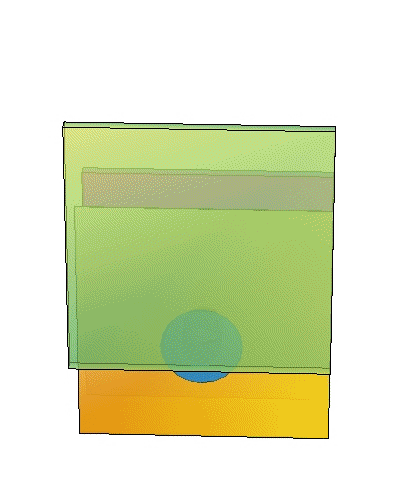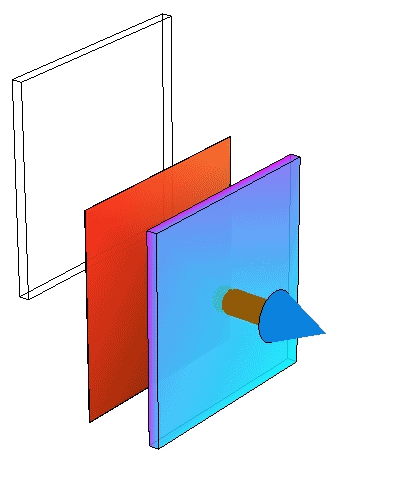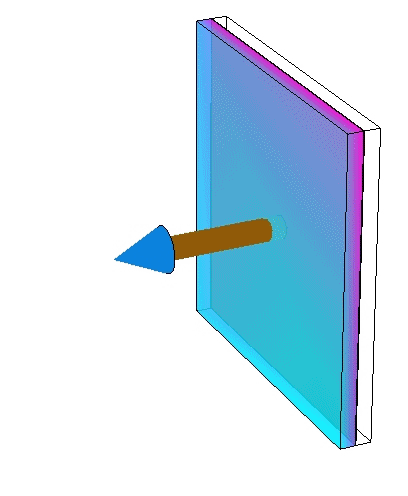 |  |
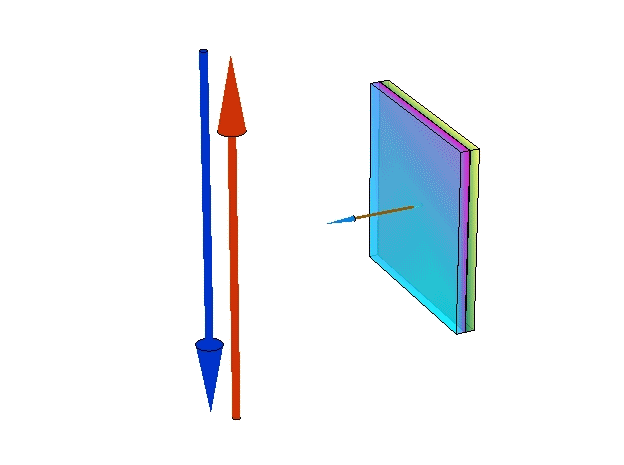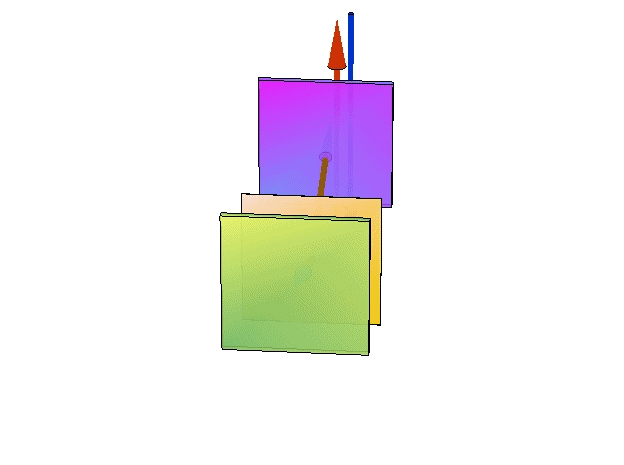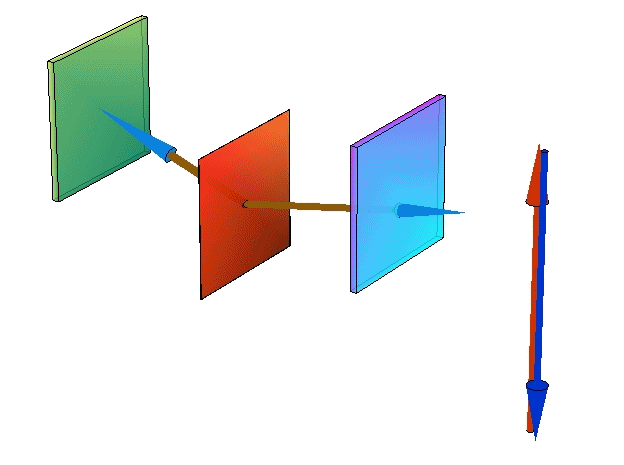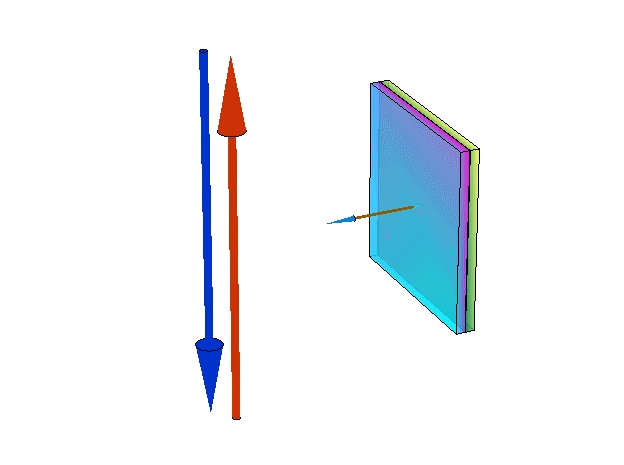
Changing chemical potentials
| reality | conservative | even more conservative |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 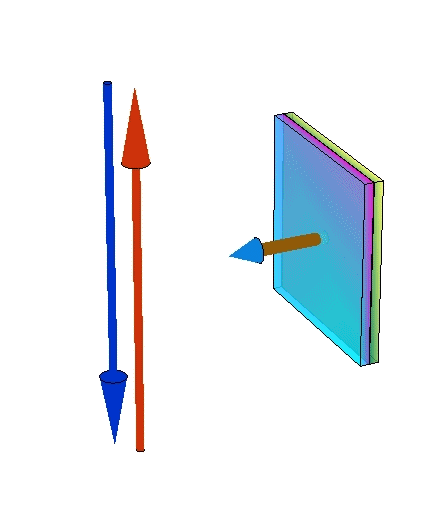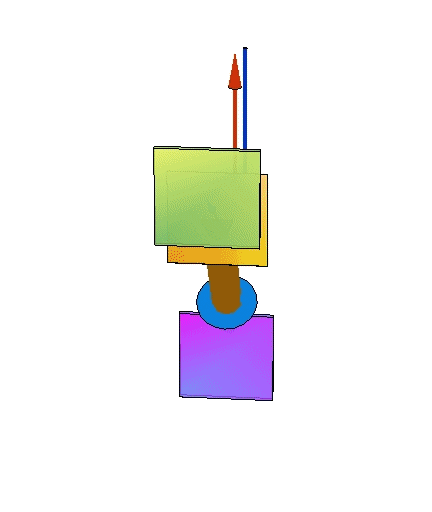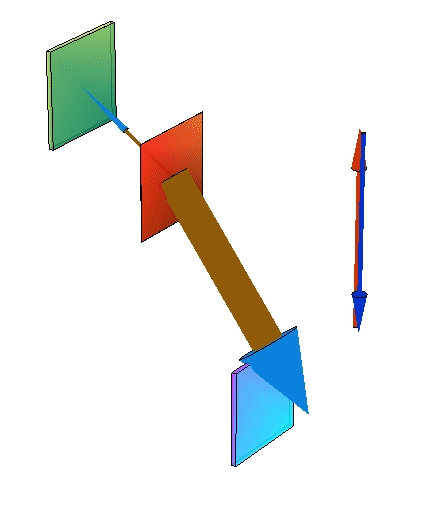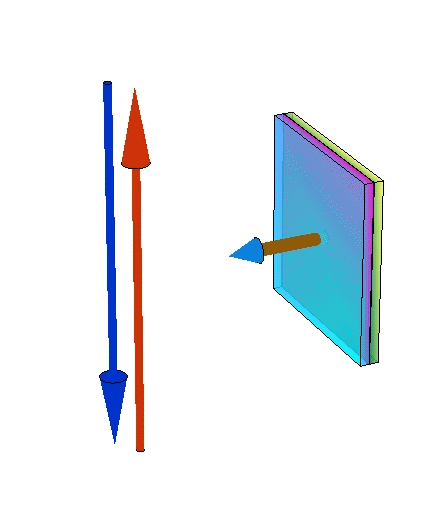 |
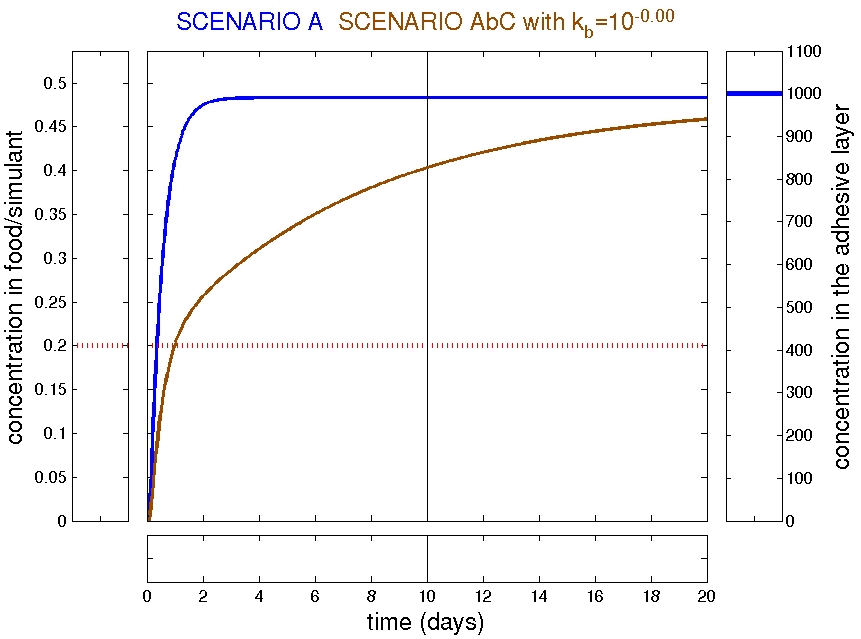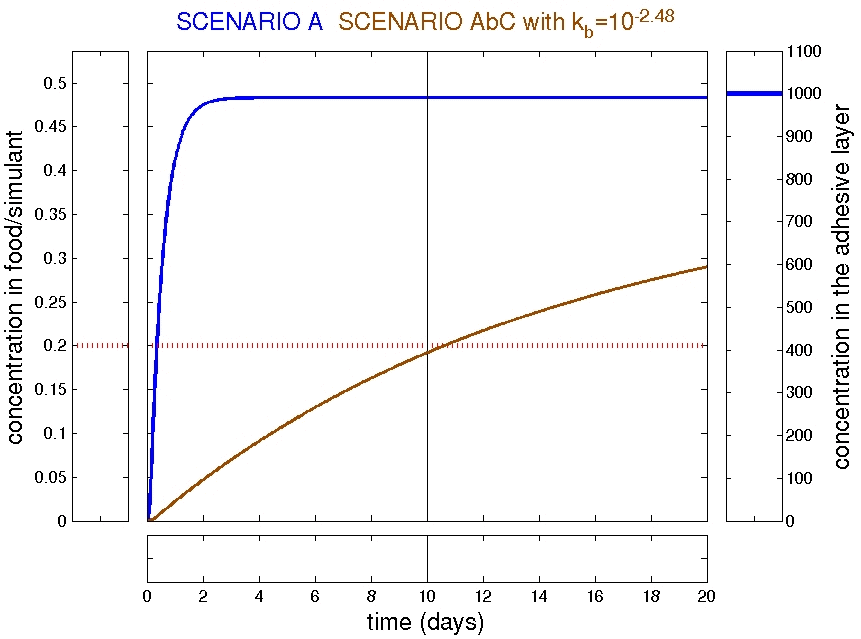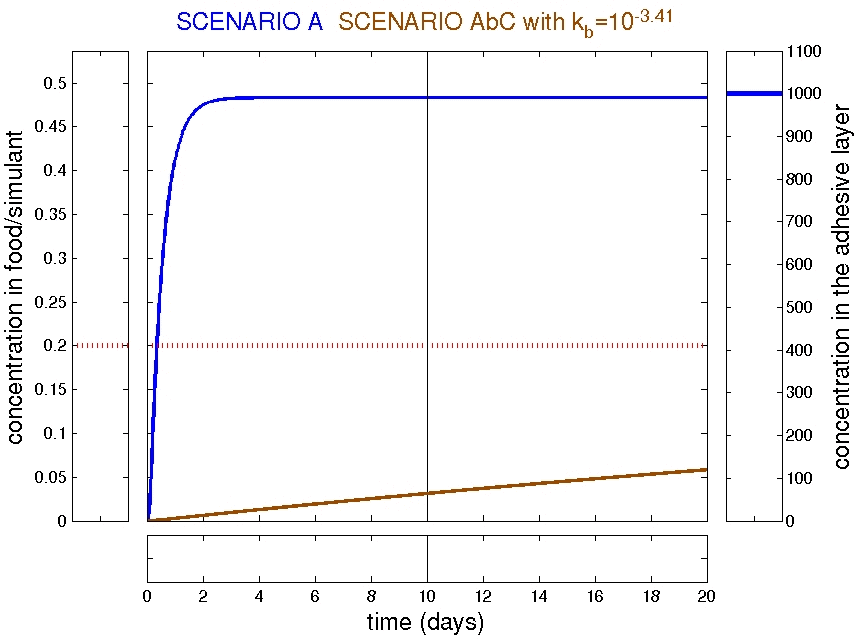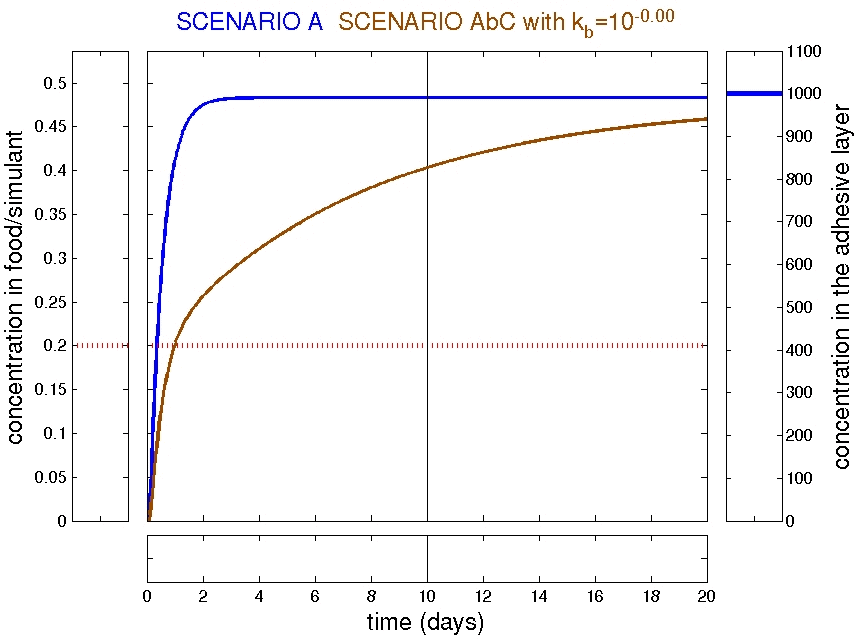
Examples: trilayer AbC
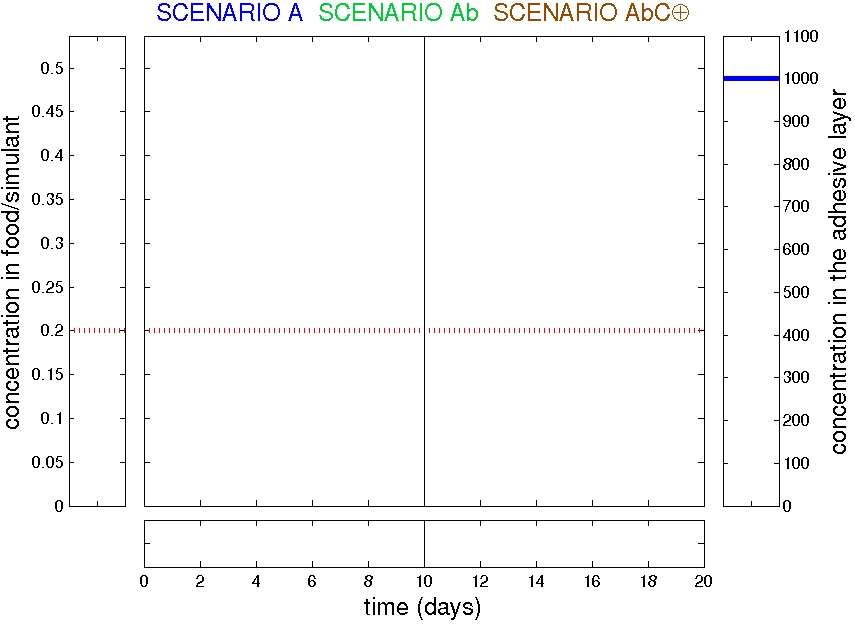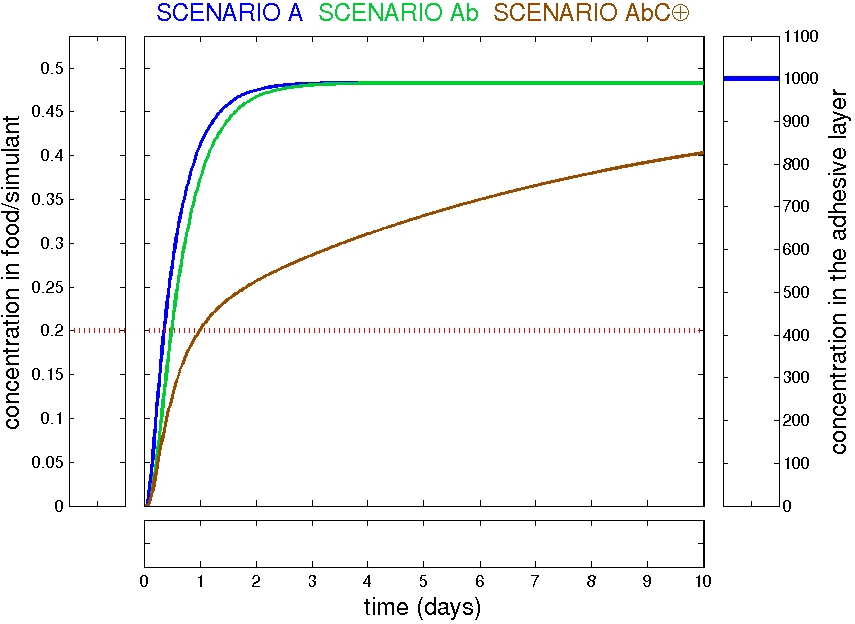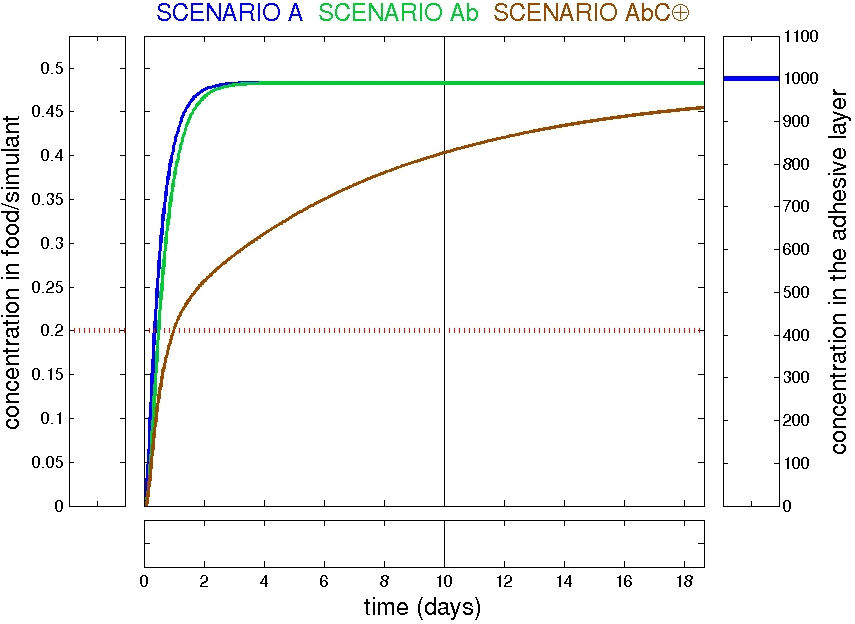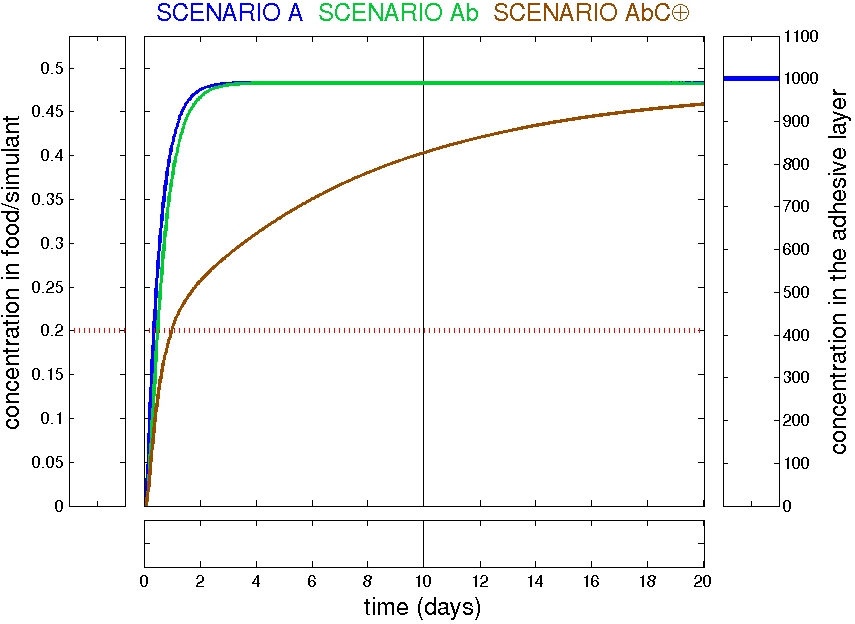
Refined scenarios: trilayer AbC
 |  |